Page Contents
- 1 What are electric hydronic baseboard heaters?
- 2 How do electric hydronic baseboard heaters work?
- 3 What are the pros of electric hydronic baseboard heaters?
- 4 What are the cons of electric hydronic baseboard heaters?
- 5 How energy efficient are electric hydronic baseboard heaters?
- 6 How does the cost of heating with electric hydronic baseboard heaters compare to other heating methods?
- 7 Conclusion
What are electric hydronic baseboard heaters?
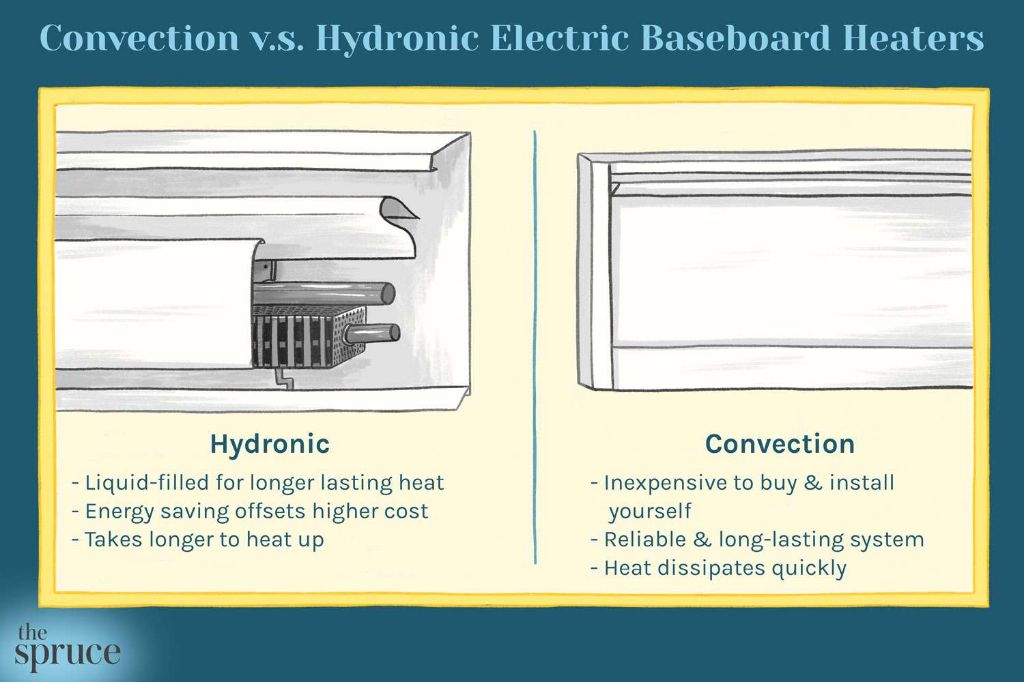
Electric hydronic baseboard heaters are a type of electric heater that uses hot water to provide heat in a home. They consist of a long metal enclosure that runs along the base of walls in a room. Inside the enclosure is a electric heating element, a piping system, and often a small fan. Water from the home’s water heater circulates through the piping system where it is warmed by the heating element before moving to baseboards throughout the home. As the warmed water moves through the baseboard units, the heat is radiated out into the room either through convection as the water transfers heat to the metal enclosure, and in some models, by a fan that helps blow the heat out into the room.
How do electric hydronic baseboard heaters work?
An electric hydronic baseboard heating system works like this:
1. Water from the home’s electric, gas, oil, or solar water heater is pumped through a closed loop pipe system that connects to the baseboard heaters throughout the home.
2. Inside each baseboard unit is an electric heating element. As the water from the water heater passes through the piping inside the baseboard, the electric element heats the water further.
3. The now heated water transfers its heat to the metal enclosure of the baseboard heater through conduction. The warmed metal enclosure then radiates heat into the room through convection.
4. In some models, a small electric fan helps blow air across the warmed enclosure to help transfer heat into the room through forced convection.
5. Once the water passes through the entire circuit of baseboard heaters, it cycles back to the water heater to be reheated before making the loop again.
6. Thermostats control each baseboard unit separately to maintain the desired temperature in individual rooms. When the thermostat calls for heat, it sends power to turn on the heating element.
So in summary, an electric hydronic system uses electricity to heat water that is then distributed through the home to deliver warmth through a series of baseboard heaters. The hydronic system simply uses hot water to carry heat instead of relying solely on electric resistance heating elements.
What are the pros of electric hydronic baseboard heaters?
Here are some of the main benefits of using electric hydronic baseboard heaters:
– Energy efficient – Hydronic systems transfer heat very efficiently. Less heat is lost compared to forced air systems.
– Zonal heating – Each room can be controlled independently to optimize heating and save energy.
– No ductwork – Avoid energy losses associated with leaky or improperly insulated ductwork.
– Minimal maintenance – With no moving parts, hydronic systems require less maintenance.
– Quiet operation – No noisy blower fan needed.
– Cleanliness – No blowing around of dust with a central forced air system.
– Adjustable positioning – Baseboard units can be positioned wherever heat is needed most.
– Even heating – Hydronic systems provide consistent, even heating throughout the home.
– Long lifespan – Quality baseboard units can last for decades.
– No draftiness – Unlike forced air systems, no cold drafts or temperature fluctuations.
What are the cons of electric hydronic baseboard heaters?
There are also some downsides associated with electric hydronic baseboard heating:
– Higher upfront costs – Installation costs are usually higher compared to forced air.
– Limited airflow – No circulation of air which could lead to stagnation or moisture buildup.
– Limited climate control – Only provides heating, no cooling or humidity control. Need separate A/C system.
– No filtering – Unlike central air, no filtration of air particles and allergens.
– Limited aesthetics – Baseboard units are fairly utilitarian and plain looking.
– Inflexible positioning – Baseboards must be located on exterior walls and can limit furniture positioning.
– Inoperable during power outages – Will not provide heat when the power is out.
– Possible boiler issues – Problems with water heater performance can cripple the system.
– Tripping hazards – Low profile of units can create tripping hazard.
– Accessibility concerns – Can make some maintenance tasks more difficult.
– Higher water usage – Circulating pumps use more water than forced air systems.
So the main limitations have to do with higher upfront costs, lack of climate control features, accessibility issues, and dependence on the water heater.
How energy efficient are electric hydronic baseboard heaters?
The energy efficiency of an electric hydronic heating system depends on several factors:
– **Efficiency of the heating element** – The electric resistance heating elements inside the baseboard units convert 100% of their electricity into heat. However, older systems may have outdated, inefficient heating elements. Newer models can be near 100% efficient.
– **Insulation** – Well insulated baseboard units prevent heat loss to the wall and back of the heater. Newer models have more insulation.
– **Thermostat control** – Having zonal control allows each room to be heated only as needed. This optimization saves energy.
– **Boiler efficiency** – An inefficient water boiler wastes heat during the creation and transfer of hot water. Look for models over 90% efficient.
– **Distribution efficiency** – Minimal heat loss from leaks and proper insulation of the distribution piping maximizes delivered heat.
– **Home insulation** – Like any system, an energy efficient building envelope reduces heat loss and energy usage.
According to the Department of Energy, a modern electric hydronic system properly designed for a well-insulated home can provide heat at 90% efficiency or greater. Gas boiler systems tend to be slightly more efficient at around 95% efficiency. Compare this to a forced air furnace which averages around 80% efficiency.
How does the cost of heating with electric hydronic baseboard heaters compare to other heating methods?
Here is a comparison of estimated heating costs for a typical 2000 sq ft home using different heating systems:
| Heating System | Fuel Source | Annual Heating Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Gas Furnace | Natural Gas | $580 |
| Propane Furnace | Propane | $920 |
| Oil Furnace | Heating Oil | $1200 |
| Standard Electric Furnace | Electricity | $1400 |
| Electric Hydronic Boiler | Electricity | $950 |
| Electric Hydronic Baseboard | Electricity | $1080 |
Assumptions:
– Modern, properly sized and installed equipment
– Energy costs of $0.12/kWh for electricity, $1.25/gal for propane, $3.00/gal for oil, and $0.85/therm for natural gas
– Climate similar to Chicago, IL
Key takeaways:
– Natural gas is generally the cheapest heating option
– Heat pumps can also be very cost effective options
– Hydronic systems are typically cheaper to operate than forced air
– Electric baseboard and furnace systems are 2-3x more expensive than gas
– Propane and oil prices can fluctuate significantly by season and region
Consider both the installation cost and the long term energy expenses when choosing a heating system. Get multiple quotes and speak to an energy auditor for advice on your specific home. Proper sizing, insulation and thermostat settings also impact real world costs.
Conclusion
Electric hydronic baseboard heating systems can be an energy efficient and comfortable heating option, especially in homes not served by natural gas lines. The hydronic system uses hot water to distribute heat from room to room. When combined with properly insulated baseboards, an efficient boiler, good controls, and an energy efficient home, the operating costs can be lower than standard electric heating. However, electricity is still typically 2-3 times more expensive per BTU than natural gas. The higher installation costs and dependence on electricity are the main limitations. But for homes where adding ductwork is impractical or gas is unavailable, hydronic heating is a decent option to consider.