Acidic soil can be a challenge for gardeners, but there are ways to improve it. Soil acidity is measured on a pH scale, with a pH of 7 being neutral. A pH below 7 indicates acidic soil, while a pH above 7 indicates alkaline soil. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic soil pH of around 6.0 to 6.5. If your soil is too acidic, it can affect plant growth and nutrient uptake.
One way to improve acidic soil is to add lime. Lime is a natural mineral that raises soil pH levels. The general recommendation is to add five to ten pounds of lime per 100 square feet of garden soil to increase the pH by one level. However, if you have clay soil, it may take more lime to raise the pH. It’s important to note that adding too much lime can also be harmful, so it’s best to test your soil pH before adding any amendments.
Another way to improve acidic soil is to add organic matter. Organic matter, such as compost, manure, or leaf mold, can help to increase soil pH levels and improve soil structure. It’s recommended to add one to two inches of organic matter to the soil surface and work it into the top six inches of soil. This can be done in the fall or spring, depending on your gardening schedule. By improving the soil structure, you’ll also increase the soil’s ability to hold water and nutrients, leading to healthier plants.
Page Contents
Understanding Soil pH
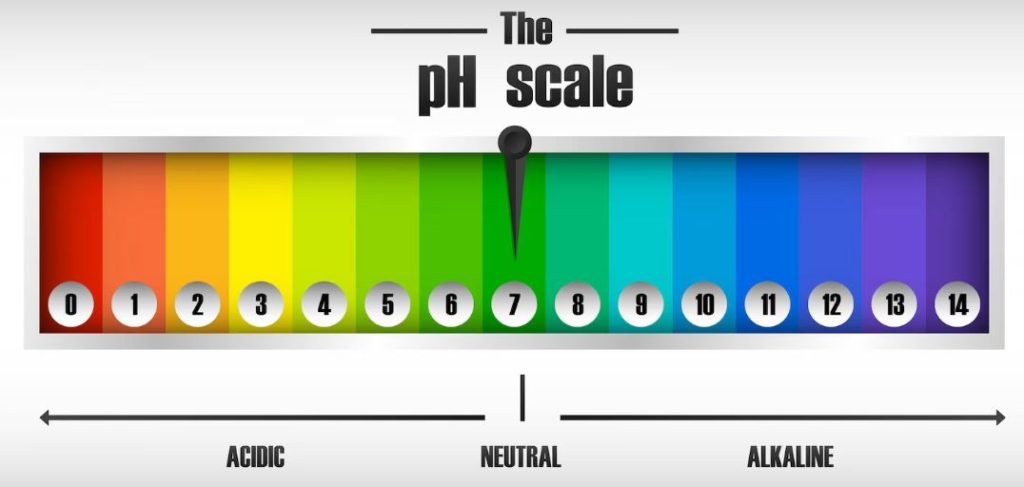
The pH Scale
Soil pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of soil. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. A pH below 7 indicates acidic soil, while a pH above 7 indicates alkaline soil.
Acidic Soils
Acidic soils have a pH below 7.0. They are commonly found in areas with high rainfall or where the soil is naturally acidic. Acidic soils can cause problems for plants because they can make nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium less available to plants.
Neutral Soils
A pH of 7.0 is considered neutral. Neutral soils are generally considered ideal for most plants because they allow for the best nutrient availability.
Alkaline Soils
Alkaline soils have a pH above 7.0. They are commonly found in dry regions or areas with high levels of limestone or other alkaline minerals. Alkaline soils can also cause problems for plants because they can make certain micronutrients less available.
Understanding soil pH is important for gardeners because it affects the availability of nutrients to plants. Different plants have different pH preferences, so it’s important to test your soil pH before planting and adjust it if necessary. Adding lime to acidic soil can raise the pH, while adding sulfur can lower it.
It’s important to note that soil pH can vary within a single garden bed. Different areas of the bed may have different pH levels, so it’s important to test multiple areas and average the results. Additionally, some plants can tolerate a wider range of pH levels than others.
Overall, understanding soil pH is an important part of gardening. By testing and adjusting your soil pH, you can ensure that your plants have access to the nutrients they need to grow and thrive.
Identifying Acidic Soil

Acidic soil can be detrimental to the health and growth of plants in your garden. It is important to identify whether your soil is acidic or not before taking any corrective measures. In this section, we will discuss two ways to identify acidic soil: soil testing and signs of acidic soil.
Soil Testing
Soil testing is the most accurate and reliable method to determine the pH level of your soil. It can also help identify any mineral deficiencies in the soil that may be contributing to the acidity. A soil test kit can be purchased at a garden center or online. The kit will include instructions on how to collect a soil sample and perform the test.
The ideal pH level for most garden plants is between 6.0 and 7.0. If the pH level is below 6.0, the soil is considered acidic. If the pH level is above 7.0, the soil is considered alkaline. The soil test results will also provide information on the amount of nutrients present in the soil, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Signs of Acidic Soil
There are several signs that can indicate acidic soil in your garden. These signs include:
- Poor plant growth: Plants may grow slowly or not at all in acidic soil.
- Yellowing leaves: Leaves may turn yellow due to mineral deficiencies caused by the acidity.
- Stunted growth: Plants may be smaller than normal due to the lack of nutrients.
- Weeds: Acidic soil can promote the growth of certain weeds, such as sorrel and dock.
- Soil color: Acidic soil may have a reddish or yellowish color.
If you notice any of these signs in your garden, it is important to perform a soil test to confirm whether the soil is acidic or not. Once you have identified acidic soil, you can take corrective measures to improve the soil pH level and promote plant health.
Effects of Acidic Soil on Plants
Acidic soil, with a pH level below 7, can have detrimental effects on the growth and health of plants. In this section, we will discuss the effects of acidic soil on plants, including nutrient absorption, plant growth, and plant health.
Nutrient Absorption
One of the primary effects of acidic soil on plants is that it can inhibit their ability to absorb essential nutrients from the soil. In acidic soil, nutrients such as phosphorus, calcium, and magnesium become less available to plants. This can lead to nutrient deficiencies, which can cause stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and poor plant health.
Plant Growth
Acidic soil can also have a negative impact on plant growth. Plants that are grown in acidic soil may experience stunted growth, reduced flower and fruit production, and overall poor performance. This is because acidic soil can limit the availability of nutrients that plants need to grow and thrive.
Plant Health
In addition to nutrient deficiencies and stunted growth, acidic soil can also make plants more susceptible to disease and pests. Plants that are grown in acidic soil are more likely to develop root rot, which can be fatal. Additionally, acidic soil can burn plants, causing damage to their roots and leaves.
To combat the effects of acidic soil on plants, gardeners can take steps to improve the pH of their soil. This may include adding lime or other alkaline materials to the soil, or planting acid-loving plants that are better suited to acidic soil conditions. By taking these steps, gardeners can help ensure that their plants grow and thrive, even in acidic soil conditions.
Improving Acidic Soil

If you have acidic soil in your garden, your plants may be struggling to grow and thrive. Fortunately, there are several ways to improve the pH level of your soil and create a more hospitable environment for your plants.
Adding Lime
One of the most common ways to improve acidic soil is by adding lime. Lime is a soil amendment made from limestone or calcium carbonate and can help raise the pH level of your soil. The general recommendation for adding lime to your soil is to add five to ten pounds per 100 square feet of garden soil to increase your soil’s pH by one level. However, if you have clay soil, it will take more than the prescribed level to raise your pH.
There are different types of lime available, including hydrated lime and dolomitic lime. Hydrated lime is faster-acting than dolomitic lime but can be more expensive. Dolomitic lime contains both calcium and magnesium, which can be beneficial for some plants.
Organic Matter and Compost
Adding organic matter and compost to your soil can also help improve its pH level. Organic matter, such as leaves, grass clippings, and kitchen scraps, can help increase the pH level of your soil over time. Compost, on the other hand, can help improve the structure and fertility of your soil, making it easier for plants to grow.
When adding organic matter or compost to your soil, it’s essential to mix it thoroughly to ensure that it’s evenly distributed. You can also add a layer of organic matter or compost to the top of your soil and let it break down over time.
Soil Amendments
In addition to lime and organic matter, there are several other soil amendments that you can use to improve the pH level of your soil. Wood ash, for example, is a natural source of potassium and can help raise the pH level of your soil. Minerals such as gypsum and Epsom salts can also be used to improve soil structure and nutrient availability.
When choosing a soil amendment, it’s essential to consider the specific needs of your plants and the current state of your soil. Some amendments, such as topsoil and organic material, can help improve soil structure and fertility but may not directly impact pH levels.
Improving the pH level of your soil takes time and patience, but with the right approach, you can create a healthy and productive garden. By adding lime, organic matter, and other soil amendments, you can create a more hospitable environment for your plants and enjoy a bountiful harvest.

Choosing Plants for Acidic Soil
When it comes to gardening in acidic soil, it’s important to choose plants that thrive in a lower pH environment. Here are some options for trees, shrubs, flowers, perennials, vegetables, and fruits that are well-suited for acidic soil.
Trees and Shrubs
There are plenty of trees and shrubs that prefer acidic soil. Conifers, such as pine, spruce, and fir, are good options, as are pink hydrangeas, azaleas, and rhododendrons. These plants not only tolerate acidic soil, but they also benefit from it.
Flowers and Perennials
Many acid-loving plants are also popular flowers and perennials. Blueberries, cranberries, and other members of the heath family are good choices, as are camellias, daffodils, and irises. These plants not only tolerate acidic soil, but they also benefit from it.
Vegetables and Fruits
While most vegetables and fruits prefer a more neutral pH, there are a few that do well in acidic soil. Potatoes, sweet potatoes, and yams are good options, as are tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants. Blueberries, cranberries, and strawberries are also well-suited for acidic soil.
When choosing plants for an acidic garden, it’s important to consider their specific needs and growing conditions. By selecting plants that are well-suited for acidic soil, gardeners can ensure healthy, vibrant growth and a beautiful, thriving garden.
Regional Considerations for Acidic Soil
 When it comes to improving acidic soil in your garden, it’s important to consider the regional climate and soil composition. Different regions have different soil types and environmental factors that can affect the acidity of the soil. In this section, we’ll take a look at some of the regional considerations for acidic soil in the Pacific Northwest, Midwest, and West.
When it comes to improving acidic soil in your garden, it’s important to consider the regional climate and soil composition. Different regions have different soil types and environmental factors that can affect the acidity of the soil. In this section, we’ll take a look at some of the regional considerations for acidic soil in the Pacific Northwest, Midwest, and West.
Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest is known for its wet climate, which can lead to acidic soil. The region’s soil is typically high in organic matter, which can contribute to acidity. To improve acidic soil in the Pacific Northwest, gardeners can add lime or wood ash to the soil. However, it’s important to note that adding too much lime or wood ash can raise the pH too high, which can also be detrimental to plant growth.
Midwest
The Midwest is known for its fertile soil, but it can also be prone to acidity. The region’s soil is typically high in clay, which can contribute to acidity. To improve acidic soil in the Midwest, gardeners can add lime or wood ash to the soil. It’s important to note that the amount of lime or wood ash needed will depend on the soil’s pH level. Sandy soils will require less lime or wood ash than clay soils.
West
The West is known for its dry climate, which can lead to alkaline soil. However, some areas in the West, such as the Pacific Northwest, can have acidic soil. To improve acidic soil in the West, gardeners can add lime or wood ash to the soil. It’s important to note that the amount of lime or wood ash needed will depend on the soil’s pH level.
Climate Crisis
It’s worth noting that the climate crisis can also affect soil acidity. Rising temperatures and changes in precipitation patterns can alter the pH of the soil. In some cases, the soil may become more acidic, while in others, it may become more alkaline. As such, it’s important to monitor soil pH regularly and adjust as needed to ensure optimal plant growth.
Overall, improving acidic soil in your garden requires careful consideration of regional factors such as climate and soil composition. By adding lime or wood ash as needed, gardeners can adjust the pH of the soil and promote healthy plant growth.

Preventing Acidic Soil
Preventing acidic soil in your garden is crucial to ensure that your plants thrive. Here are some tips to help prevent acidic soil:
Proper Fertilization
Using commercial or synthetic fertilizers can lead to soil acidity. Therefore, it is essential to use organic fertilizers that break down slowly, releasing nutrients to the soil over time. For example, bone meal and blood meal are excellent organic fertilizers that can help prevent soil acidity. It is also important to avoid over-fertilization, as this can lead to nutrient imbalances that can cause soil acidity.
Avoiding Overwatering
Overwatering can cause soil acidity, especially in areas with heavy rainfall. When the soil is waterlogged, it can lead to the depletion of oxygen, which can cause the growth of bacteria that produce acids. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that the soil is well-drained and that the plants are not overwatered.
Regular Soil Testing
Regular soil testing is essential to prevent soil acidity. It helps to determine the pH level of the soil, which can help determine the type of fertilizer needed. Soil testing can also help detect nutrient deficiencies that can lead to soil acidity. It is recommended to test the soil every three years.
Preventing acidic soil is essential for maintaining soil fertility and plant health. By following these tips, gardeners can ensure that their plants thrive and that the soil remains healthy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which fertilizer increases the acidity of soil?
Fertilizers that contain ammonium sulfate, sulfur-coated urea, or elemental sulfur can increase the acidity of soil. Ammonium sulfate is the most commonly used fertilizer for this purpose. It is recommended to apply the fertilizer in small amounts and mix it well with the soil. It is important to note that overuse of these fertilizers can harm plants and soil.
How to make soil acidic for rhododendrons?
Rhododendrons thrive in acidic soil with a pH level between 4.5 and 6.0. To make soil acidic for rhododendrons, gardeners can mix organic matter such as peat moss, sawdust, or pine needles into the soil. It is recommended to mix one-third organic matter with two-thirds soil. Gardeners can also use sulfur-based fertilizers to lower the pH level of the soil. It is important to test the soil pH level before and after adding any amendments to ensure that the pH level is within the desired range for rhododendrons.

