Running low voltage wiring for 12v circuits is a common need for many projects. Whether you are installing landscape lighting, audio speakers, security cameras, or other low voltage accessories, determining how far you can run the wiring is key to a successful installation.
Page Contents
Quick Answer
For most 12v DC low voltage wiring applications, you can run the wiring up to 100 feet with minimal voltage drop and loss of power. However, there are many factors that come into play that can influence how far you can run 12v wiring including:
- Wire gauge – Thicker wire allows for longer runs
- Power requirement – Higher power devices need thicker wire for long runs
- Number of devices – More devices require thicker wire
- Environment – Outdoor runs need thicker wire than indoor
With the right wire gauge and power considerations taken into account, it is possible to run 12v low voltage wiring up to 200 feet or more, especially indoors. Outdoor runs may need to be limited to 100 feet or less.
Voltage Drop
The main limitation on how far you can run 12v low voltage wire is voltage drop. Voltage drop refers to the reduction in voltage that occurs as power is transmitted along a wire. Some amount of voltage drop is inevitable when running 12v wire. The longer the run, the greater the drop in voltage along the way due to the resistance in the wire.
Significant voltage drop can cause problems for 12v circuits by providing devices with inadequate voltage. Generally a voltage drop of more than 10% (1.2 volts on a 12v circuit) is considered unacceptable and can cause issues.
The amount of voltage drop that will occur depends on:
- Wire gauge – Thicker wire has less resistance and less drop.
- Wire length – Longer runs have more drop than shorter runs.
- Current draw – More current through the wire causes more drop.
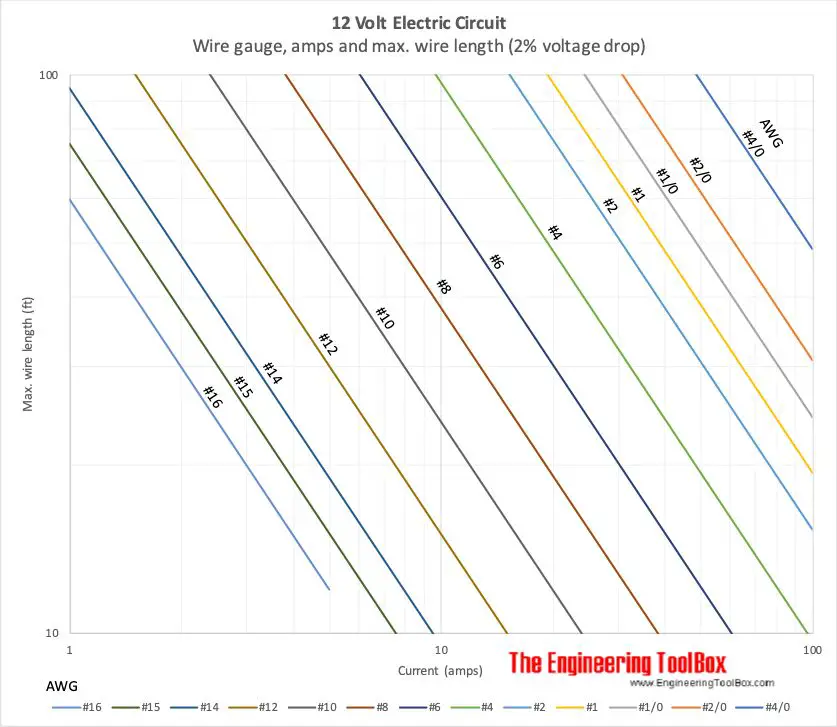
Recommended Maximum Run Length by Wire Gauge
Here are some general recommendations for the maximum run length that can be used based on wire gauge when running 12v low voltage wiring:
| Wire Gauge | Maximum Recommended Run Length |
|---|---|
| 22 AWG | 25 feet |
| 20 AWG | 50 feet |
| 18 AWG | 75 feet |
| 16 AWG | 125 feet |
| 14 AWG | 200 feet |
These run lengths are based on limiting voltage drop to 10% when running a moderate 12v load of 3 amps. Heavier power demands would require thicker wire and/or shorter runs.
Tips for Longer Run Lengths
If you need to run 12v wiring beyond the recommended maximum distances, there are a few things that can help extend the maximum run:
- Use thicker wire than required – Increasing wire gauge allows for longer runs before voltage drop becomes an issue.
- Reduce power demands – Use less power-hungry devices on the circuit to reduce current flow.
- Use power supplies with higher voltage – A 24v system will have lower drop than 12v over the same distance.
- Use lower current lighting – LEDs, for example, use less power than other options.
- Inject additional power – Using a booster power supply partway through the run can boost voltage.
Taking steps like these can allow you to stretch 12v low voltage wiring to run up to 200 feet or even longer in some cases, especially indoors.
Outdoor Runs
Outdoor low voltage wiring runs have additional challenges to consider. Running wire outdoors requires using wire that is rated for direct burial and wet locations. The ground and moisture can dissipate heat and decrease conductivity compared to indoor wire runs.
For these reasons, it is recommended to limit outdoor 12v runs to no more than 100 feet with most wire gauges. To run wiring long distances outdoors, thicker wire gauges like 12 AWG or 10 AWG may be required.
Connecting Multiple Devices
When running a single 12v device like a security camera or landscape light, it is fairly simple to determine the maximum wire run length based on the power demand. However, many low voltage projects require running multiple devices on a single circuit.
Each device added to the circuit increases the total power demand and current. This additional current causes more voltage drop along the wire run. To compensate when connecting multiple devices, you may need to use a thicker wire gauge than would be required for a single device.
As a general guideline, if you need to run more than 3 or 4 low voltage devices on a single circuit, plan to use a wire gauge 2 sizes thicker than the minimum recommended for a single device. For example use 14 AWG rather than 18 AWG.
Low Voltage Wire Types
There are a few main options when selecting wire for 12v low voltage circuits:
- Standard multi-strand copper wire – Used for indoor runs. Available in a range of gauges.
- High strand count silicone wire – Flexible option used for things like PC case wiring.
- CCA wire – Copper Clad Aluminum rated for direct burial. Used for outdoor runs.
- THHN wire – For running in conduit. More rugged insulation.
Using the proper type of wire for the specific application ensures safe installation and reliability. Indoor applications can use standard copper wire while outdoor runs are better served by burial-rated CCA wire.
Voltage Drop Calculators
To precisely determine the voltage drop for a specific run, you can use a voltage drop calculator. These tools allow you to input the wire gauge, run length, and power requirements. It will then calculate the voltage drop percentage that will result.
Online calculators and mobile apps can provide voltage drop figures quickly. These tools remove the guesswork and allow you to input different scenarios to determine the maximum run length for your low voltage project wiring.
Conclusion
12v low voltage wiring can typically run 100 feet for most general applications. However, the specific wire gauge, power demands, and environmental factors need to be taken into account to determine the maximum distance for a particular installation. With adequate wire sizing and voltage drop considerations, 12v wiring runs can often reach 200 feet or more, allowing you to power devices even at longer distances from the power supply.