A silt fence is a temporary sediment control device used on construction sites to protect water quality in nearby streams, rivers, lakes and seas from sedimentation. Silt fences prevent soil erosion and capture sediment-laden runoff from disturbed areas by filtering out sediment and decreasing the velocity of runoff. They serve as a barrier to intercept and detain sediment while allowing water to percolate through. Silt fences are made of woven geotextile fabric attached to supporting posts and trenched into the ground. When installed properly and maintained, silt fences can be highly effective at controlling erosion and retaining sediment on site during construction activities.
Page Contents
Main Uses of Silt Fences
Silt fences have three key uses on construction sites:
1. Prevent Soil Erosion
Silt fences function as a barrier to intercept and pond runoff, reducing its velocity and erosive potential. This allows sediment to settle out behind the fence through filtration and sedimentation. Silt fences protect soil from being detached and transported off site by surface water flows, wind or mechanical equipment. They are placed below disturbed areas on slopes and around site perimeters to control erosion.
2. Capture Sediment
By temporarily ponding runoff, silt fences allow time for sediment to settle out of the water. Sediment is trapped behind the fence as water seeps through the porous fabric. This prevents sediment-laden runoff from leaving the construction site and entering water bodies. Silt fences remove sediment from runoff through filtration and sedimentation processes.
3. Protect Water Bodies
Silt fences prevent sediment from moving offsite and impacting nearby streams, rivers, lakes, wetlands and oceans. Sedimentation can degrade water quality by increasing turbidity, reducing light penetration and smothering aquatic habitat. Silt fences placed between disturbed areas and water bodies intercept runoff and remove sediment before it reaches receiving waters. This protects sensitive aquatic ecosystems from the negative effects of construction site erosion and sedimentation.
Where are Silt Fences Installed on Construction Sites?
Silt fences are installed in key locations on construction sites to maximize their effectiveness at controlling erosion and sedimentation, including:
Downslope of Disturbed Areas
Silt fences are placed along the perimeter of disturbed land downgradient of slopes and construction activities. This captures runoff and sediment from areas exposed by grading, excavation, vegetation removal and other ground disturbances.
Around Site Boundaries
Silt fences installed around the lower site perimeter contain sediment and prevent it from leaving the property. They protect adjacent lands and water bodies from sedimentation runoff coming off the construction area.
Near Water Bodies
Silt fences are critical around the edges of creeks, streams, rivers, ponds and lakes. They create a barrier to filter out sediment from runoff immediately adjacent to water bodies that are highly vulnerable to sedimentation impacts.
Below Cleared Areas
After clearing and grubbing removes protective vegetation, silt fences below freshly cleared slopes or site sections retain soil exposed to erosion by rainfall. This keeps sediment on site until vegetation or stabilization measures are established.
Around Drainage Inlets
Silt fences placed around storm drain inlets and culverts prevent sediment-laden runoff from entering drainage systems off site. Inlet protection measures like these keep sediment from being conveyed downstream through stormwater pipes and channels.
Proper Installation of Silt Fences
To work effectively, silt fences must be properly installed using these key steps:
Select Appropriate Location
Determine suitable positions on the contours of slopes to intercept runoff based on the site’s drainage patterns. Consider fence height and ponding capacity to handle anticipated flows.
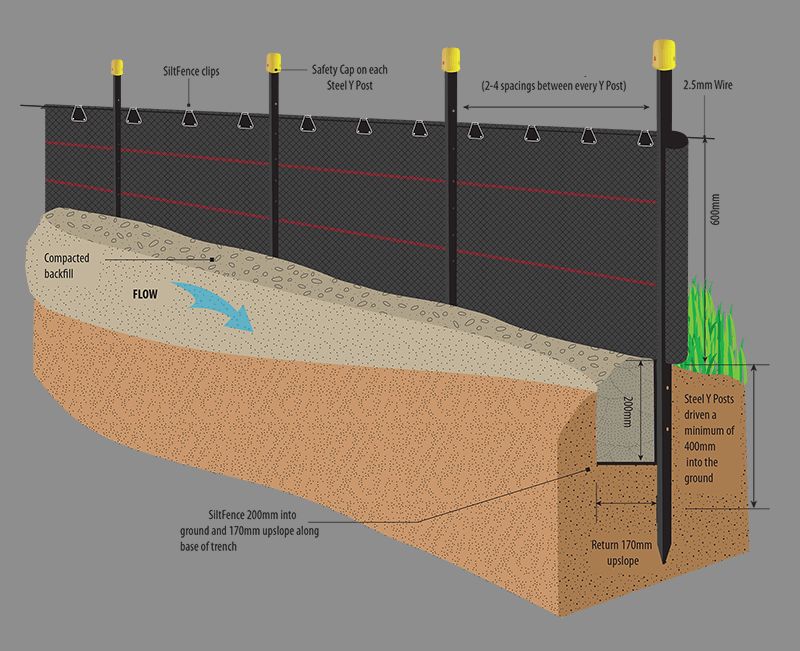
Dig Trench and Embed Fabric
Dig a 6-8 inch trench and embed the bottom 1-2 feet of the geotextile fabric in the ground. This anchors the fence and prevents undercutting below it.
Secure Support Posts
Install support posts on the downhill side no more than 6 feet apart. Attach the fabric securely to posts with staples, zip ties or other ties.
Backfill and Compact Soil
Backfill the uphill side of the trench over the silt fence fabric with compacted soil to prevent piping and underflows beneath the fence.
Overlap and Join Fabric
Where sections of fabric join, overlap the fabric by at least 6 inches. Join them together securely by folding over ends or using fasteners.
Extend Ends Up Slopes
Extend the ends of silt fence sections up the slope contours to prevent end-arounds. Turn them uphill at least 10 feet at a 45 degree angle.
| Installation Step | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Select appropriate location | Intercept runoff based on drainage |
| Dig trench and embed fabric | Anchor fence and prevent undercutting |
| Secure support posts | Attach fabric securely to posts |
| Backfill and compact soil | Avoid piping and underflows |
| Overlap and join fabric | Connect sections without gaps |
| Extend ends up slopes | Prevent runoff going around ends |
Maintenance for Proper Silt Fence Function
Routine maintenance is essential to ensure silt fences continue working properly, including:
Inspect Fences Frequently
Inspect silt fences often, especially after rain events. Look for damage, undercutting, overtopping and areas where sediment has built up excessively. Identify necessary repairs.
Remove Accumulated Sediment
Remove sediment deposits before they reach half the fence height. Otherwise overflow and underflow may occur during storms. Safety remove and dispose of sediment properly off site.
Repair Damaged Sections
Promptly repair any torn fabric, loose posts, breached areas or slumping fence sections. This prevent failure or bypassing of damaged areas during subsequent storms.
Replace Deteriorated Fabric
Replace silt fence fabric that has worn out, become weathered and brittle or no longer provides needed filtration. Old fabric allows sediments to pass through.
Prevent Sediment Bypassing
Check for flows going around fence ends and undercutting below the fabric. Repair these areas to prevent uncontrolled sediment discharges off site.
Special Applications of Silt Fences
Beyond their standard implementation, silt fences can also be used in some specialized ways, such as:
Check Dams
Silt fences can be installed perpendicular across swales or drainage ditches to function as small check dams. This slows flows and promotes settling of sediment.
Inlet Protection
Silt fences can provide temporary inlet protection when fitted around storm drain openings. This filters sediment from water entering the drainage system.
Streambank Protection
Silt fences anchored close to streambanks help stabilize eroding banks and capture sediment washing into watercourses.
Wind Screening
As wind barriers and screens, silt fences can reduce wind erosion across exposed areas such as material stockpiles or finished grading areas awaiting stabilization.
Vehicle Tracking Control
Silt fences help confine vehicle movements to designated site access routes. This prevents disturbances to protected or restored areas.
Importance of Proper Installation and Maintenance
When silt fences are improperly installed or maintained, their effectiveness at controlling erosion and sedimentation decreases dramatically. Some key points include:
Inadequate Anchoring
Silt fences that are not trenched and buried adequately become dislodged and allow flows underneath. This results in uncontrolled runoff and sediment discharges off site.
Poor Fabric Selection
Using a fabric that is too permeable allows excess water flow through while retaining little sediment. More impermeable fabrics can clog and cause bypass flows or failure.
Improper Tie-Ins
Gaps at joints between silt fence sections or tie-ins along slopes can result in concentrated flows that cause erosion or bypass the fence completely.
Lack of Maintenance
Silt fences that are damaged, weathered or filled with sediment require maintenance to remain functional. Ignoring needed repairs results in erosion and sedimentation.
Inadequate Size
Silt fences that are too short or under-designed for the size of the disturbed drainage area allows overtopping and blowouts during larger storms.
End-Arounds
Silt fences not extended upslope at ends can allow runoff to bypass going around the sides, carrying sediment off site.
Alternatives to Silt Fences
There are other sediment control practices that may be preferable alternatives to silt fences in some situations:
Wattles
Wattles are tubular sediment barriers made from straw, coir or other biodegradable materials. They are more flexible options appropriate for some areas.
Vegetated Buffers
Natural vegetated filter strips slow and filter runoff while also avoiding the maintenance needs of silt fences. But they require more space on site.
Berms
Compacted earth berms can be used to reroute and channel flows to treatment areas or sediment basins in some cases.
Rock Filters
Small rock or stone filters function like silt fences but allow higher flows while retaining sediment. Useful for concentrated flow paths.
Sediment Traps
Small temporary sediment traps or basins provide enhanced volume storage for retaining sediment and controlling concentrated flows.
Flocculants
Chemical flocculants introduced in runoff coagulate suspended sediment particles to improve settling and filtration.
The Bottom Line
Properly installed and maintained silt fences are an extremely useful erosion and sediment control device on construction sites. They intercept runoff, slow velocities and retain sediment on site to prevent soil loss and protect water quality. Silt fences help control erosion and prevent sedimentation impacts when placed appropriately downhill of disturbed areas and near water bodies. Routine maintenance to fix any damage and remove accumulated sediments keeps silt fences working effectively throughout the construction process. With attention to proper installation and maintenance practices, silt fences provide an excellent line of defense against erosion and sedimentation problems.