A silt fence is a temporary sediment control device used on construction sites to prevent soil erosion and sedimentation. Silt fences are designed to filter and trap sediment-laden runoff from disturbed areas, preventing it from leaving the site and polluting nearby waterbodies. They serve an important purpose in controlling erosion and complying with environmental regulations.
Page Contents
- 1 Why are silt fences used?
- 2 Where are silt fences installed on a construction site?
- 3 How does a silt fence work to control erosion?
- 4 What are the components of a silt fence system?
- 5 What are the main installation steps?
- 6 What maintenance is required?
- 7 What are common silt fence failures?
- 8 What are typical specifications for silt fence fabric?
- 9 What are recommended silt fence installation guidelines?
- 10 What are common mistakes made when installing silt fences?
- 11 How long can silt fences remain in place and effective?
- 12 When should silt fences be removed?
- 13 Can silt fences be made more sustainable?
- 14 Conclusion
Why are silt fences used?
Silt fences are a key tool used by contractors and engineers for controlling soil erosion and runoff on construction sites. There are several important reasons silt fences are installed:
- To comply with environmental regulations – Many local, state, and federal laws require erosion and sediment control measures on construction sites. Silt fences help meet these regulatory requirements.
- To prevent sediment from leaving the site – By filtering runoff, silt fences trap soil particles and prevent them from being transported off the site. This protects nearby storm drains, ditches, streams, and other waterbodies.
- To control erosion – Silt fences slow and spread out the flow of runoff, preventing rill and gully erosion on disturbed slopes and areas.
- To allow settlement of sediment – By temporarily ponding runoff behind the fence, particles are given time to settle out before the runoff is released.
- To limit impacts on adjacent properties – Silt fences contained sediment on the construction site, preventing damage to neighboring properties.
When installed and maintained properly, silt fences provide an effective barrier to sediment movement on active construction sites. They help control erosion, minimize environmental impacts, and contain sediment-laden runoff.
Where are silt fences installed on a construction site?
Silt fences are strategically installed in key areas on a construction site to maximize their effectiveness. Typical locations include:
- Along the perimeter of the site – To prevent sediment from leaving the property and impacting adjacent lands.
- Below disturbed slopes and soils – To capture runoff and trap sediment before it can accumulate at the base of slopes.
- Around temporary stockpiles – To contain erosion from material stockpiles that are prone to runoff.
- Above sensitive areas – To divert runoff away from streams, wetlands, or preserves.
- Along channels and drainages – To filter out sediment from runoff before it enters drainage ways.
- Around inlets and storm drains – To prevent sediment-laden runoff from entering drainage systems offsite.
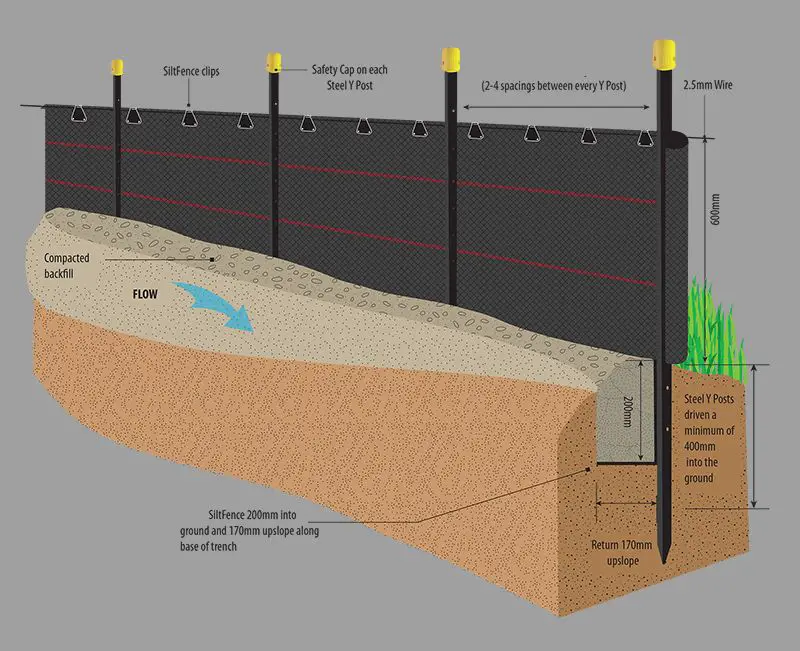
The accompanying diagram shows a typical silt fence installation on a construction site:
| Location | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Site perimeter | Contain runoff and sediment within site |
| Below slopes | Capture erosion from disturbed soils |
| Around stockpiles | Prevent material erosion into runoff |
| Above sensitive areas | Divert flows away from offsite features |
| Along drainages | Filter sediment before runoff leaves site |
| At storm drains | Protect inlets from sediment accumulation |
Proper placement is key for silt fences to work effectively. A qualified engineer should evaluate the site and design the layout.
How does a silt fence work to control erosion?
Silt fences use a simple filtration mechanism to trap and retain sediment from runoff. The process works as follows:
- Stormwater runoff flows towards the silt fence from disturbed soils and slopes.
- The runoff passes through the geotextile fabric, which acts as a filter to remove sediment.
- The fence posts provide support and temporarily pond water behind the fabric, slowing flow.
- The slowed, ponded water allows soil particles to settle out by gravity behind the fence.
- The filtered runoff water passes through the fabric at a reduced velocity after temporary ponding.
- Trapped sediment builds up behind the fence and is periodically removed to maintain effectiveness.
This simple process results in removal of up to 80% or more of the sediment from runoff before it can leave the construction site. The fence acts as a barrier, filter, velocity reducer, and sediment trap.
What are the components of a silt fence system?
A typical silt fence installation consists of several components working together to filter runoff:
- Geotextile fabric – The filter material made of woven or nonwoven polypropylene, nylon, polyester geotextile. It has openings sized to trap sediment particles.
- Fence posts – Typically metal or hardwood stakes installed to provide support to the geotextile fabric. They give the fence stability.
- Fabric embedding – A 6 to 12-inch section of fabric buried in the ground to prevent underflows.
- Reinforced bottom – An extra layer of fabric or wire mesh to strengthen the bottom against water pressure.
- Backing support – A plastic or wire mesh backing provides additional support on longer fence runs.
- Fasteners – Zip ties, wire, or stapes used to securely fasten the fabric to the fence posts and any backing support.
When assembled together according to standard designs, these components create an effective filtration barrier. Proper installation is critical for the fence to function.
Design and Specifications
Silt fences are designed and sized to suit specific site conditions and runoff volumes. Typical specifications include:
| Parameter | Typical Specification |
|---|---|
| Fabric type | Woven or nonwoven geotextile, 10 to 20 oz./sq. yd density |
| Fabric width | 24 to 36 inches |
| Fabric tensile strength | 100 to 300 lb grab tensile strength |
| Maximum post spacing | 6 to 8 feet |
| Maximum slope length | 100 feet for slopes <2% steep |
| Maximum ponding depth | 1.5 feet at lowest point |
A designer tailors these specifications to match the fence strength and ponding requirements.
What are the main installation steps?
Proper installation techniques are critical for silt fences to function effectively. Key installation steps include:
- Select appropriate location based on site plan.
- Excavate a 6 to 12-inch deep trench along installation line.
- Drive stakes at least 16-inches into the ground on downhill side.
- Attach fabric to stakes using zip ties, leaving a 2 to 3-inch flap extending into trench.
- Backfill and compact the trench, embedding fabric flap into soil.
- Secure fabric skirt tightly to ground with stakes spaced as specified.
- Where ends meet, overlap fabric 6 to 12 inches allowing for continuity.
- Inspect regularly and repair any damage, tears, or undercutting.
Proper installation ensures the fence filters and retains sediment from runoff. Poor installation can lead to underflows and failure.
What maintenance is required?
Routine maintenance is essential to keep silt fences functioning properly throughout a project. Typical silt fence maintenance includes:
- Inspecting for damage after storm events and repairing as needed.
- Checking for tears, loose fabric, and collapsed sections.
- Removing accumulated sediment when it reaches 6 inches deep.
- Replacing deteriorated fabric sections.
- Installing additional stakes for sagging or slumping fences.
- Improving ponded water drainage if flows bypass the fence.
- Ensuring the fabric skirt remains buried and backed into soil.
With proper maintenance, a silt fence can remain effective for up to 6 months. Neglected fences have reduced effectiveness and can fail.
What are common silt fence failures?
When poorly installed or maintained, silt fences are prone to certain modes of failure that compromise their effectiveness:
- Undercutting – Erosion below fence skirt creates an opening for underflows.
- Overtopping – Inadequate height causes flows to exceed fence capacity and bypass over top.
- Collapse – Improper burial and lack of backing allows fence to fall over and create openings.
- End flow – Gaps at joints and ends allows runoff to bypass around sides.
- Material failure – Low strength fabric tears under pressure, creating holes and openings.
- Lack of maintenance – Accumulated sediment and damage reduces filtration ability over time.
Careful installation, design, and maintenance helps prevent these failure modes.
What are typical specifications for silt fence fabric?
Silt fence fabric, also called geotextile, provides the filtration capability and strength. Typical specifications require:
- Geotextile fabric material: Polypropylene, nylon, polyester woven or nonwoven.
- Fabric roll width: 24 to 36 inches wide to minimize seams.
- Fabric strength: Minimum 100 lb grab tensile and burst strengths.
- Openings or apparent opening size: Pass #30 sieve, 0.01-0.024 inch openings.
- Permittivity/permeability: 0.05 – 0.2 sec-1 to allow adequate water flow.
- Ultraviolet resistance: Minimum 70% strength retained after 500 hours exposure.
- Flow rate: Varies, typically 10 to 20 gpm/sf for temporary installations.
Heavy duty fabrics with high strength and appropriate opening sizes perform the best. Designers select geotextiles suited to site conditions.
What are recommended silt fence installation guidelines?
To achieve effective performance, silt fences should be installed following these key guidelines:
- Fences should be placed along level contours to facilitate ponding.
- Maximum slope steepness perpendicular to fence is 1:1.
- Turn ends of fence uphill to prevent end flow.
- Leave no gaps at joints between sections.
- Excavate a 6 to 12-inch deep trench and embed fabric skirt.
- Provide sufficient post spacing and backing support for conditions.
- Inspect regularly and repair any damage immediately.
- Remove sediment before it exceeds 6 inches depth.
- Do not allow water depth to exceed 1.5 feet at lowest point.
Strict adherence to manufacturer and design specifications is recommended for proper installation.
What are common mistakes made when installing silt fences?
Some of the most common silt fence installation errors that compromise performance include:
- Not embedding the fabric skirt deep enough into the ground.
- Leaving gaps between sections or at ends.
- Allowing water to pool too high behind the fence.
- Improper orientation to slope contours.
- Inadequate post spacing or backing support.
- Poor joint fastening and overlap.
- Not removing accumulated sediment in time.
- Using low strength or inappropriate fabric.
- Failing to inspect and repair damage after storms.
- Not ensuring proper drainage to prevent bypass flow.
Careful construction according to specifications prevents these installation issues.
How long can silt fences remain in place and effective?
With proper maintenance, silt fences can remain effective erosion and sediment controls for extended periods when needed. Typical effective lifespans are:
- 3 to 6 months for initial installation.
- Up to 1 year if maintained and repaired as needed.
- 2 years or longer for semi-permanent installations.
The useful life depends on factors like weathering, ultraviolet exposure, sediment loading, and damage potential. Regular inspection and maintenance is key for long-term performance.
When should silt fences be removed?
Silt fences should be removed when they are no longer needed for erosion and sediment control. Typical conditions indicating silt fence removal include:
- Site soils are stabilized with vegetation or other cover.
- All disturbed areas draining to the fence are permanently stabilized.
- Construction activity that exposes soil has ceased.
- Other permanent stormwater controls are in place.
- The fence has reached the end of its functional lifespan.
Ideally, silt fences are removed once the drainage area has stabilized and the risk of erosion has passed. The materials should be disposed of properly.
Can silt fences be made more sustainable?
Traditional plastic-based silt fence materials pose sustainability challenges. However, new options exist to make them more eco-friendly:
- Biodegradable fabrics – Made from natural fibers or biopolymers that decompose after use.
- Recycled plastics – Polypropylene and PET fabrics made from recycled bottles or other plastics.
- Renewable materials – Fabrics derived from sustainable sources like coconut fiber or industrial hemp.
- Reusable designs – Durable systems that can be cleaned and reinstalled multiple times.
- Natural stabilizers – Vegetation, mulch, or compost that can replace synthetic materials.
These and other emerging technologies offer the potential for more sustainable and environmentally-friendly silt fence options in the future.
Conclusion
Silt fences serve the vital purpose of controlling erosion and protecting water quality on construction sites. When properly installed and maintained, they can effectively filter sediment from runoff and prevent it from leaving disturbed areas. A basic filtering mechanism allows silt fences to trap soil particles and allow clean water to flow through. Following design guidelines and specifications, installing with care, and performing regular maintenance ensures silt fences remain functional. New materials and options provide promise for more sustainable solutions while still serving the important role silt fences play in erosion and sediment control.